Introduction
The processes in all organisms—from bacteria
to humans—require energy. To get this energy, many organisms
access stored energy by eating, that is, by ingesting other
organisms. But where does the stored
energy in food originate? All of
this energy can be traced back to photosynthesis.
Overview of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is essential to all life on earth; both plants and animals depend on it. It is the only biological
process that can capture
energy that originates in outer space (sunlight) and convert it into chemical
compounds (carbohydrates) that every organism uses to power its metabolism. In brief, the energy of sunlight is captured and used to
energize electrons, which are then
stored in the covalent bonds of sugar molecules. How long lasting and stable
are those covalent bonds? The energy
extracted today by the burning of coal and petroleum products represents
sunlight energy captured and stored
by photosynthesis almost 200 million years ago.
Plants, algae, and a
group of bacteria called cyanobacteria are the only organisms capable of performing photosynthesis (Figure 1.1). Because they use light to manufacture their own food, they are called photoautotrophs (literally, “self-feeders
using light”). Other organisms, such
as animals, fungi, and most other bacteria, are termed heterotrophs (“other feeders”), because they
must rely on the sugars produced by photosynthetic organisms for their energy
needs. A third very interesting group of bacteria synthesize sugars, not by
using sunlight’s energy,
but by extracting energy from inorganic chemical compounds; hence, they are referred to as chemoautotrophs.
Figure
1.1 Photoautotrophs including (a) plants, (b) algae, and (c) cyanobacteria synthesize their organic compounds
via photosynthesis using sunlight
as an energy source. Cyanobacteria and planktonic algae can
grow over enormous areas in
water, at times completely covering the surface. In a (d) deep sea vent, chemoautotrophs, such as these (e) thermophilic bacteria, capture energy from inorganic compounds
to produce organic compounds.
The ecosystem surrounding the vents has
a diverse array of animals, such as tubeworms, crustaceans, and
octopi
that
derive energy from the bacteria. (credit a: modification
of work by Steve Hillebrand, U.S. Fish and
Wildlife Service; credit b: modification of work by "eutrophication&hypoxia"/Flickr; credit c: modification of work by NASA; credit d: University
of Washington, NOAA; credit e: modification of work by Mark Amend,
West Coast and Polar Regions Undersea Research Center, UAF, NOAA)
The importance of
photosynthesis is not just that it can capture sunlight’s energy. A lizard sunning itself on a cold day
can use the sun’s energy to warm up. Photosynthesis is vital
because it evolved as a way to store the energy
in solar radiation (the “photo-” part) as high-energy electrons in the carbon-carbon bonds of carbohydrate
molecules (the “-synthesis” part). Those carbohydrates are the energy source that heterotrophs use to power
the synthesis of ATP via
respiration. Therefore, photosynthesis powers 99 percent of Earth’s ecosystems. When a top predator, such as a wolf,
preys on a deer (Figure 1.2),
the wolf is at the end of an energy path that went from nuclear
reactions on the surface of the sun, to light,
to photosynthesis, to
vegetation, to deer, and finally to wolf.
Figure
1.2 The energy stored
in carbohydrate molecules from photosynthesis passes through the food chain.
The predator that eats these deer receives a portion
of the energy that originated in the photosynthetic vegetation that the deer consumed. (credit: modification of work by Steve VanRiper,
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service)
Main Structures and Summary of Photosynthesis
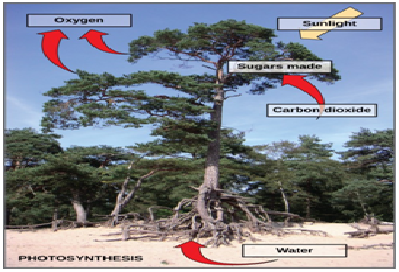
Photosynthesis is a
multi-step process that requires sunlight, carbon dioxide (which is low in energy), and water as substrates (Figure 1.3). After
the process is complete, it releases oxygen
and produces glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GA3P), simple carbohydrate molecules
(which are high in energy) that can
subsequently be converted into glucose, sucrose, or any of dozens of other
sugar molecules. These sugar molecules contain energy and the energized
carbon that all living things need to survive.
Figure
1.3 Photosynthesis uses solar energy, carbon dioxide, and water to produce energy-storing carbohydrates. Oxygen is generated as a
waste
product of photosynthesis.
The following is
the chemical equation for photosynthesis (Figure 1.4):
Figure
1.4
The basic equation for photosynthesis is
deceptively simple. In reality,
the process takes place
in many steps involving intermediate reactants and products. Glucose,
the primary energy source in
cells, is made from two three-carbon GA3Ps.
Although the equation looks
simple, the many steps that take place
during photosynthesis are actually quite
complex. Before learning the
details of how photoautotrophs turn sunlight into food, it is important to
become familiar with the structures involved.
In plants, photosynthesis
generally takes place in leaves, which consist of several layers of cells. The
process of photosynthesis occurs in a middle layer called the mesophyll. The gas exchange of carbon
dioxide and oxygen occurs through small, regulated
openings called stomata (singular: stoma), which also play roles in the regulation of gas exchange and water balance. The stomata
are typically located on the underside of the leaf, which helps to minimize
water loss. Each stoma is flanked by guard cells that regulate the opening and
closing of the stomata by swelling or shrinking in response to osmotic changes.
In all autotrophic
eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place inside an organelle called a chloroplast. For plants, chloroplast-
containing cells exist in the mesophyll. Chloroplasts have a double membrane
envelope (composed of an outer membrane and an inner membrane). Within the chloroplast are stacked,
disc-shaped structures called thylakoids.
Embedded in the thylakoid membrane is chlorophyll, a pigment (molecule that absorbs light) responsible for the initial
interaction between light and plant
material, and numerous
proteins that make up the electron transport chain. The thylakoid membrane encloses an
internal space called the thylakoid
lumen. As shown in Figure 1.5, a stack of thylakoids is called a granum, and the liquid-filled space surrounding the granum is called stroma or “bed” (not to be confused
with stoma or “mouth,” an opening
on the leaf epidermis).
Figure 1.5 Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, which have an outer
membrane and
an inner membrane. Stacks of
thylakoids called
grana
form a third membrane layer.
On a hot, dry day, plants close their stomata
to
conserve water. What impact will
this have on photosynthesis?
The Two Parts of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in two sequential
stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light independent-reactions. In the light-dependent
reactions, energy from sunlight is absorbed by
chlorophyll and that energy is
converted into stored chemical energy. In the light-independent reactions, the chemical energy harvested
during the light-dependent reactions drive the assembly of sugar molecules from carbon
dioxide. Therefore, although the light-independent reactions do not use light as a reactant,
they require the products of the light-dependent reactions to function.
In addition, several
enzymes of the light-independent reactions are activated by light. The light-dependent reactions utilize certain molecules to temporarily store
the energy: These are referred to as
energy carriers. The energy carriers that move energy from light-dependent reactions to
light-independent reactions can be thought of as “full” because they are rich
in energy. After the energy is
released, the “empty” energy carriers return
to the light-dependent reaction to obtain more energy. Figure 1.6 illustrates the
components inside the chloroplast where the light-dependent and
light-independent reactions take place.
Figure
1.6 Photosynthesis takes place in two stages: light dependent reactions
and the Calvin cycle. Light-dependent
reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membrane, use light energy to
make ATP and
NADPH. The Calvin
cycle, which takes place in the stroma, uses energy derived from these compounds
to make GA3P from CO2.